Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABS) is a game-changing technology in the world of digital video streaming. As modern entertainment enthusiasts avoid traditional cable or satellite and prefer cord-cutting solutions such as IPTV and OTT streaming, Intelligent Bitrate Switching becomes an essential part of streaming.
Since it adjusts video quality based on internet speed, it is crucial for people living in rural areas where a fast connection is not available.
The main target of ABR is to ensure viewers can enjoy streaming seamlessly; there shouldn’t be any buffering or lagging. ABR makes it happen by dynamically adapting the stream quality in real time to match available bandwidth and device capabilities. This is how it can ensure a smooth streaming experience for the users.
ABS works for both live and on-demand content, but it’s significant for live streaming—where sports fans and PPV viewers rely on smooth, buffer-free performance in real time.
In this article, I’ll delve into the work methods of ABS, its benefits and challenges, and how to implement it in your streaming service. Let’s not prolong this here and get into the main discussion.
What is Adaptive Bitrate Technology?
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming is a method of delivering video where the source content is encoded at multiple bitrates. The streaming player automatically switches between these streams to provide the best possible viewing experience, depending on internet speed and device performance.
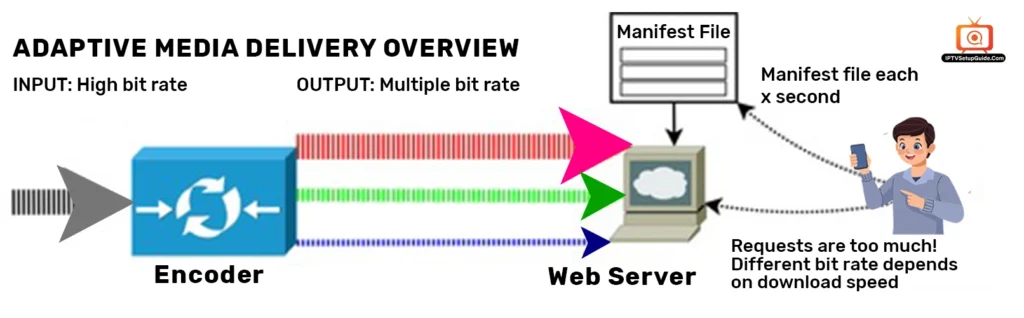
This Dynamic Bitrate Streaming tech ensures seamless playback while reducing buffering. Thus, users can enjoy the best possible streaming quality.
How does Adaptive Streaming Technology Work?
Adaptive bitrate streaming generally relies on the 5 steps shown below. Let’s check:
1. Multi-Bitrate Encoding
The main video is encoded into multiple versions (bitrates and resolutions). For example:
- 1080p – 6 Mbps
- 720p – 3 Mbps
- 480p – 1.5 Mbps
- 360p – 800 Kbps
- 240p – 400 Kbps
2. Video Segmentation
Each version is chunked into short segments (2–10 seconds). This allows the media player to leap between quality levels quickly.

3. Creating Evident File
An evident player generates:
- .m3u8 for HLS
- .mpd for MPEG-DASH
This file contains a structured list of all available bitrates.
4. Client-Side Adaptive Algorithm
Modern IPTV apps use algorithms that measure: current bandwidth, device CPU/GPU capability, buffer health, and network fluctuations. The player then fetches the best segment available at that moment.
5. Real-time Switching
If the connection somehow drops, the player instantly switches to a lower bitrate. When the network improves, streaming quality can improve. The switching moments are short! People can enjoy smooth streaming.
Advantages and Challenges of Dynamic Streaming Technology
So, what are the benefits and potential challenges of using ABS? Look at this:
Benefits of ABR
- No Buffering – With the network bandwidth detection technology in Internet TV Provider services or OTT platforms, viewers can enjoy seamless streaming without buffering. No wonder most top-notch IPTV subscription providers and OTT streaming services offer this technology to their users.
- Platform Compatibility – The highly sophisticated ABS technology is compatible across all platforms, including Android-based IPTV apps, Smart TVs (Samsung Tizen, LG webOS), Browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari), Mobile apps (iOS/Android).
- Well-balanced Experience – Users can enjoy the best possible streaming, depending on the internet speed.
- Highest Performance – Ensures a more enhanced and top-quality streaming compared to static streaming methods.
Challenges of ABR
- Multiple video versions: ABS requires encoding the same video in many resolutions and bitrates. Therefore, the processing work increased.
- Higher storage needs: More video files mean more storage space on servers or CDNs.
- Increased server load: Handling multiple streams at once can strain bandwidth and server resources.
- Latency issues: Some ABS protocols (like HLS) can add delays, especially during live streaming.
- Player compatibility: The video player must support fast and smooth bitrate switching on different devices.
What Streaming Protocols Support Adaptive Bitrate Streaming?
Streaming protocols that support Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABS) primarily include:
- HTTP Live Streaming (HLS): Developed by Apple, HLS is the most widely used adaptive streaming protocol. It is compatible with most devices and browsers, including Apple devices. It allows streaming of video in multiple bitrates and automatic switching based on bandwidth availability.
- Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH): Also known as MPEG-DASH, it is a codec-agnostic protocol popular for adaptive streaming across various platforms and devices. DASH provides a manifest file that lists multiple bitrate streams, allowing the player to switch streams dynamically.
- Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP): While traditionally used for video ingestion rather than adaptive streaming itself, RTMP can be part of a streaming workflow where video is ingested and then transcoded into adaptive bitrate formats like HLS or DASH.
- WebRTC: Used for low-latency and real-time streaming. WebRTC supports adaptive bitrate to maintain stream quality by dynamically adjusting the bitrates based on network conditions (slow or fast).
- Enhanced RTMP (E-RTMP): An upgraded form of RTMP that supports modern codecs like HEVC (H.265), AV1, and VVC (H.266), along with multi-bitrate streaming. Its stronger connection stability makes it ideal for interactive and real-time content.
How to Integrate Adaptive Bitrate Streaming into Your Platform?
1. Create a Multi-Bitrate Encoding Ladder
Encode your video in multiple resolutions and bitrates so the player can switch quality levels based on network conditions. This is the foundation of ABS.
2. Segment Your Video into Small Chunks
Break each version of the video into short segments (2–6 seconds).
These small pieces help the player switch bitrates instantly and smoothly.
3. Package Streams Using HLS or MPEG-DASH
Use streaming protocols like HLS or MPEG-DASH to generate manifest files (M3U8 or MPD). These files guide the video player on which bitrate levels are available.
4. Deliver Content Through a CDN
A CDN ensures your video segments are distributed globally with fast delivery, low buffering, and stable access for viewers.
5. Implement an Adaptive Player with Bitrate Switching
Use a video player that supports ABS logic to measure bandwidth, buffer size, and device capabilities, and choose the best quality in real time.
6. Add DRM and Security Measures
Integrate DRM solutions like Widevine, FairPlay, or PlayReady to protect your content across devices.
7. Optimize and Test Across Devices
Test your ABS setup on different devices, networks (Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G, Starlink), and platforms to ensure stability and smooth switching.
8. Monitor Performance with QoS/QoE Analytics
Track metrics like:
- Average delivered bitrate
- buffering time
- playback failures
- segment download speed
This helps you refine your bitrate ladder and improve user experience.
Final Words
If you’re a modern streaming enthusiast, you must know that adaptive bitrate streaming technology is essential for smooth streaming. Whether you’re watching a live Champions League match between Barcelona vs Chelsea or Real Madrid vs Liverpool or a Taylor Swift or Justin Bieber concert, you want to feel real-time fun.
The ABR technology can help you achieve it. It ensures seamless and uninterrupted streaming. This is why this technology has been adopted by all the top-notch IPTV service providers and Over-the-Top streaming services.
Applying Dynamic Streaming Technology with the perfect conditions of protocols, encoders, CDNs, and player optimizations – can elevate your IPTV or streaming watching experience to another level.
FAQs on Dynamic Bitrate Adjustment: How Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Improves Video Quality
Q – Is Adaptive Bitrate Streaming necessary for IPTV?
A – Yes. IPTV relies heavily on ABS to minimize buffering and handle different types of internet speeds. Without Adaptive Streaming Tech, it’s impossible to enjoy seamless video streaming, especially in rural areas.
Q – What is adaptive bitrate streaming on Netflix?
A – Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) on Netflix is a technology that automatically adjusts the video quality in real time based on your current internet speed. With ABS tech, Netflix users can enjoy the smoothest playback.
Q – What is the best bitrate for streaming?
A – The best bitrate depends on your streaming resolution, frame rate, and platform. Generally, higher resolutions require higher bitrates to maintain video quality, while lower resolutions use less bandwidth.
Q – Which bitrate mode is the best?
A – There is no single “best” bitrate mode. The best bitrate mode depends on your goal—quality, stability, or efficiency. The three most common bitrate modes are CBR, VBR, and CRF, each suited for different situations.
Q – Is ABS compatible with 4K streams?
A – Yes. ABS supports 4K and even 8K, as long as multiple bitrate versions are encoded.
Q – Does YouTube use adaptive streaming?
A – Yes. YouTube uses Adaptive Media Delivery tech to automatically adjust video quality based on a viewer’s internet speed, device performance, and network conditions.
Q – Which is better, adaptive high bitrate or high bitrate?
A – Adaptive High Bitrate (AHB) is generally better for streaming because it adjusts video quality automatically based on network conditions.
Q – Which bitrate is best to use?
A – The best bitrate depends on your resolution, frame rate, platform, and internet upload speed.
